Gum Disease and Other Diseases
Research has shown that periodontal disease is linked with various other diseases. For a long time it was thought that bacteria was the factor that associated periodontal disease with other diseses of the body; however, recent research shows that inflammation might be responsible for this association. As such, treating inflammation may not only help manage periodontal diseases but also help managing other chronic inflamamatory conditions.
DIABETES AND PERIODONTAL DISEASE
Diabetic patients are more prone to developing periodontal disease, which in turn might elevate blood sugar and diabetic complications.
People with diabetes are more prone to having perioodntal disease than people without diabetes, probably becasue people with diabetes are more susceptible to infections. In fact, periodontal disesase is sometimes considered a diabetic complication. Those people that do not have diabetes under control are especially at higher risk.
Research has suggested that the relation between diabetes and periodontal disease is two-way -- periodontal disease may make it harder for people with diabetes to control their blood sugar.
GUM DISEASES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
Heart Disease
Several studies have shown that periodontal disease is associated with heart disease. While a cause-and-effect relation has not been proven yet, research indicates that periodontal disease increases the risk of heart disease.
Scientists believe that inflammation caused by periodontal disease may be responsible for this association.
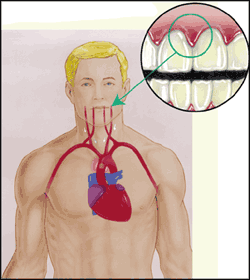
Periodontal disease may also worsen existing heart conditions. Patients at risk for infectious endocarditis may require antibiotics prior to dental procedures. Your periodontist and cardiologist may determine if your heart condition requires the use of antibiotics before dental procedures.
Stroke
Additional studies point to a relation between periodontal disease and stroke. In a study that looked at the causal relation of oral infection as a risk factor for stroke, people diagnosed with acute cerebro-vascular ischemia were found with more tendency to having oral infection when compared to the control group.
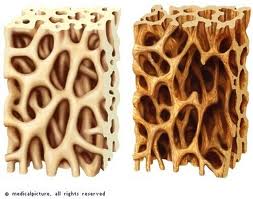
OSTEOPOROSIS
Researchers have suggested a relation between osteoporosis and bone loss of the jaw. Studies suggest that osteoporosis may lead to tooth loss because density of tooth supporting bone may decrease, which means teeth no longer have a solid foundation.
RESPIRATORY DISEASE
Research has found that bacteria growing in the oral cavity may be aspirated into the lungs to cause respiratory diseases, especially in people with periodontal disease.
CANCER
Researchers have found that men with periodontal disease are 49% more prone to developing kidney cancer; 54% more prone to develop pancreas cancer; and 30% more prone to blood cancer.
With periodontal treatment it is not only about curing bleeding gums and loose teeth, it is about giving health back to the body, health that is at risk of an important danger.
Controlling periodontal infection it can be said that we have a healthy mouth in a healthy body.




